The recent surge in on-line shopping due to COVID-19 should be no great surprise given the ease of access, wide range of choice, value for money and of course the safety and convenience that home shoppers recognise and appreciate, particularly during lockdown
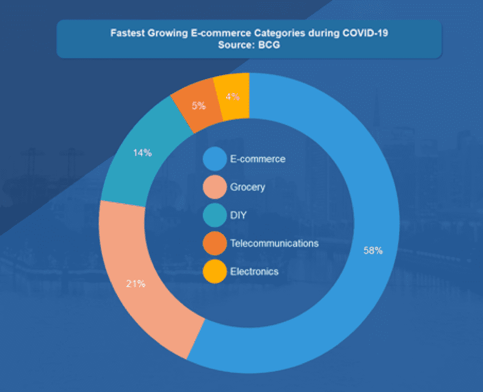
Fig 1: Fastest growing E-commerce categories during Covid-19
In terms of supply chain impact, the pandemic is the equivalent of a perfect storm where with few exceptions, most businesses have been caught off guard with business continuity plans that looked fine on paper only to fall short or entirely flat when needed. This along with a host of new requirements for social distancing and workforce protection has added more complexity, risk, and cost to already gridlocked and overburdened supply chains.
So, against this backdrop of supply chain, why has the business to consumer (B2C) or e-commerce model exploded onto the world stage? A simple web search will throw up reports explaining the underlying psychology, but the simple answer is that with time on their hands and little else to do, shoppers have been spending much more time on the web particularly social networking and gaming. Once online, the secret workings of advanced algorithms perform their product matchmaking routines to bring shoppers into direct contact with tailored brand choices from where a purchase is but one click away.
What is the e-commerce supply chain process?
The e-commerce supply chain sits poised for action beneath the surface of the web store, mostly out of sight and occasionally partially in view but maybe not immediately recognisable. The structural setup very much depends on whether the store is part of an outsourced service or not. If outsourced, it can be connected directly into the supply chain infrastructure and if not, then the connection will usually come through the seller’s order management system.
The process begins when a shopper makes a purchase on-line and that purchase is transferred to the seller’s order management database from where it is automatically transferred into the e-commerce supply chain network through the Warehouse Management System (WMS). This system control’s all activities taking place within the warehouse and sets priorities based upon order due dates and material availabilities.
Once the orders have been picked and packed (usually within 24 hours) the goods then transfer physically and systematically from the WMS to the TMS (Transportation Management System) which controls the entire process of shipping from handing over of the goods to the carriers right through to final mile delivery and POD (proof of delivery). This level of end to end system integration of WMS and TMS with the seller’s order management system is what powers the ecommerce service model and is usually equipped with multiple carriers from both parcel and postal service networks as well as advanced control tower visual dashboards and round the clock service support.
What really sets high end e-commerce apart is the integration of data analytics. There is a wide range of options available, all capable of bringing data alive in interactive and infinitely customisable ways tailored to individual user requirements. Without this analytics functionality its near impossible to manage the e-commerce supply chain experience effectively given the short cycle, lead times and high service expectations (leaving COVID-19 aside]. If you have not seen the latest data analytics applied to supply chain, then you need to do so. Seeing is believing and no further explanation is necessary. While the interconnection of seller order management with WMS and TMS is the price of entry to ecommerce the real value comes from the improved visibility and business as well as operational decision making that integrated data analytics facilitates.
Some key considerations as you continue your e-commerce journey should include:
- The concept of the Digitally Enabled Organisation where a data centric culture with analytic tools deeply embedded throughout the supply chain enable rapid response to operational circumstances and changing supply, demand, and shopper preferences.
- Opportunities to accelerate e-commerce initiatives through technology partner agreements that bolster expertise and capabilities.
- Data and technology platforms that enable complete end to end visibility of the e-commerce supply chain
Connect with us on LinkedIn to stay up to date with the latest supply chain insights
Topics from this blog: News

